Smart Contracts for Beginners: DeFi, NFT Examples & Platforms Guide
Basic Smart Contract Use Cases in DeFi and NFT
Smart contracts are the foundational logic driving the Web3 economy. Forget intermediaries; these self-executing code agreements ensure instant, trustless transactions across the globe. We demystify how this technology powers automated lending in DeFi and secures verified ownership and royalties within NFTs. What are basic smart contract use cases in DeFi and NFT? Simply put, they are the automated rules that govern everything from decentralized trading to digital asset rights. But what exactly are smart contracts used for in the broader crypto space?
DISCLAIMER: IMPORTANT NOTICE – This content is provided for informational and educational purposes only and does not constitute financial, investment, or legal advice. Smart contracts and associated digital assets (DeFi, NFTs) carry inherent significant risks, including potential loss of funds due to market volatility, coding vulnerabilities, and technical failure. You should always Do Your Own Research (DYOR), fully understand the risks involved, and consult with a qualified financial professional before making any investment decisions related to cryptocurrency or blockchain technology.
What are smart contracts used for in crypto?
Smart contracts—sounds fancy, right? Basically, they’re self-executing programs running on a blockchain, designed to handle transactions and enforce rules automatically, without middlemen. In crypto, they show up everywhere: DeFi, creating tokens, NFT marketplaces, even supply chain tracking. By embedding the rules straight into code, these contracts let people interact safely without having to trust a central authority. They speed things up, cut costs, and make everything transparent. If you’re just starting out, knowing where smart contracts fit in is key to not getting lost in the crypto jungle.
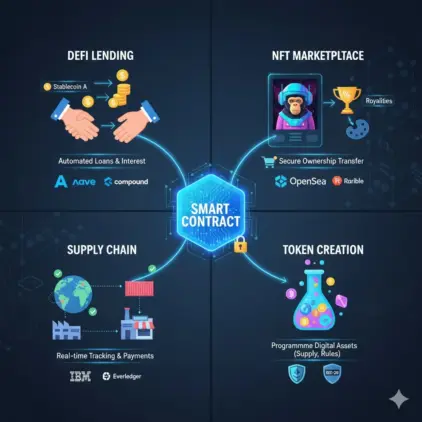
DeFi: Automating Lending, Borrowing, and Staking
DeFi? That’s where smart contracts really shine. Platforms like Aave and Compound use them to handle lending, borrowing, staking, and liquidity automatically. The contracts calculate interest rates, manage collateral, and execute loans without you lifting a finger. Users interact directly with the platform, while the code does all the heavy lifting. It’s like having a fully automated bank that never sleeps. Oh, and yield farming? Smart contracts handle that too, giving rewards according to rules you don’t even need to remember.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs) and Automated Trading
Ever used a DEX like Uniswap or SushiSwap? Smart contracts run the show there. They automatically match trades, calculate fees, and transfer tokens—all without a central order book. That means your trades are transparent and secure, and developers can craft complex strategies without needing a broker. Liquidity pools? Also handled by smart contracts. They reward users for providing tokens and keeping the ecosystem running smoothly. Honestly, it’s kind of magical once you see it in action.
How smart contracts enable token creation
Creating tokens is another playground for smart contracts. On Ethereum or Binance Smart Chain, contracts define the rules: total supply, transfer logic, distribution mechanisms—you name it. Standards like ERC-20 or BEP-20 keep tokens consistent across wallets and exchanges. Without contracts, token behavior could be unpredictable or even manipulable. Developers can also add nifty features like automatic fee distribution, staking rewards, or governance functions, turning a simple token into a lively, interactive ecosystem.
NFTs: Minting, Royalties, and Marketplace Logic
NFTs owe a lot to smart contracts. They manage minting, buying, and selling digital assets, making sure ownership transfers correctly and creators get their royalties automatically. Contracts also verify authenticity and prevent double-spending. Platforms like OpenSea or Rarible rely on smart contracts for auctions, bids, and escrow-like functions, keeping everything transparent and secure. For creators and collectors alike, smart contracts simplify the whole NFT experience.
Blockchain Tracking in Supply Chain Management
Even supply chains are getting a blockchain upgrade. Smart contracts track goods, confirm deliveries, and trigger payments automatically. Companies like Everledger or IBM Food Trust use them to increase transparency and fight fraud. From origin to destination, contracts check provenance and enforce compliance, reducing mistakes and speeding up operations. In industries like pharma or luxury goods, smart contracts help guarantee authenticity and meet regulations—making the whole chain more trustworthy and efficient.
Smart contract platforms for beginners
Picking a smart contract platform is huge when you’re starting in crypto. Ethereum is still the big player: tons of documentation, a buzzing developer community, and access to countless dApps. You can play with ERC-20 tokens, NFTs, and DeFi protocols—all in one ecosystem. Sure, gas fees can sting, but Layer 2 solutions and testnets like Rinkeby or Goerli let you experiment without burning cash. For new devs, understanding the trade-offs between speed, cost, and ecosystem maturity is essential if you want your contracts to actually work in the real world.

Why choose Ethereum for smart contracts?
Ethereum gives a mature, stable environment for building smart contracts. Tools like Truffle, Hardhat, and Remix make creating, testing, and deploying contracts easier. With broad adoption, applications can work together seamlessly. Beginners also benefit from tutorials and community help everywhere. Gas fees fluctuate, sure, but the network’s reliability and security usually outweigh the cost. Learning Ethereum first is a smart move—it teaches skills you can take to other EVM-compatible networks down the road.
Binance Smart Chain (BSC) for beginners
BSC is like Ethereum’s faster, cheaper sibling. Transactions are quick and fees are low, perfect for beginners. Plus, it’s compatible with Ethereum contracts, so you can migrate projects easily. Its ecosystem is growing, from DeFi to NFTs to yield farming. Lower costs mean more room to experiment without stress, while familiar tools make learning smooth. For newcomers, BSC is a solid entry point into smart contract development with practical, real-world use.

Cardano: A secure and scalable platform
Cardano is all about security and research-driven design. Its Plutus language emphasizes correctness, minimizing bugs. Cardano suits projects where reliability is crucial, like finance or supply chains. Beginners might find it tougher to learn than Ethereum, but mastering it teaches you how to build robust, long-lasting contracts. Low fees and a focus on sustainable development also make it appealing for developers looking for secure alternatives to high-cost networks.
Solana for high-speed smart contracts
Solana is built for speed—thousands of transactions per second, thanks to Proof of History. Perfect for high-frequency trading, gaming, or microtransactions. Beginners can test contracts without worrying about costs. The ecosystem is smaller than Ethereum’s, but Solana shows how performance-focused blockchains can deliver fast, efficient smart contracts while staying decentralized and secure.
What is gas in Ethereum smart contracts?
Gas measures the computational effort needed on Ethereum. Every transaction, from transferring tokens to running a contract, consumes gas. It keeps the network fair and prevents abuse by making users pay for computation. Costs depend on operation complexity and network load. Understanding gas is crucial—ignore it, and your transaction might fail or get delayed. Trust me, I learned that the hard way on my first Ethereum deploy!

Gas price and its impact
Gas price, measured in gwei, basically decides how much you pay for each unit of gas on Ethereum. Pay more, and your transaction jumps the queue; pay less, and you might wait forever. Wallets like MetaMask are a lifesaver here, giving recommended gas prices so you can balance cost and speed. If you’re just starting, keep an eye on network congestion—overpaying is annoying, but underpaying can be even worse. Oh, and optimizing gas isn’t just about paying; writing efficient contract code and planning transactions carefully saves a lot too.
How to calculate gas for Ethereum transactions
Figuring out gas fees isn’t rocket science. You multiply the gas limit by the gas price. The gas limit is basically the max units a transaction might consume. For example, sending ETH uses 21,000 units—if gas price is 50 gwei, that’s 0.00105 ETH. Developers constantly try to write lean, optimized code to keep fees down. As a user, you can track network conditions to choose a fair fee, balancing speed and cost so your transactions actually go through. Trust me, I learned the hard way when I miscalculated my first transaction!
How to deploy a smart contract on Ethereum?
Deploying a smart contract starts with writing the code, usually in Solidity. Editors like Remix, Truffle, or Hardhat help you write, test, and compile your contracts. Once ready, you deploy to Ethereum’s mainnet or a testnet, paying the deployment cost in ETH. Using MetaMask ensures your private keys stay safe while interacting with the blockchain. A well-planned deployment avoids bugs and makes sure your contract behaves exactly as intended in the real world.
Writing smart contracts with Solidity
Solidity is the go-to language for Ethereum smart contracts, and if you know JavaScript, you’ll feel right at home. Contracts spell out rules for tokens, ownership, transactions, and conditional logic. Beginners can lean on templates and libraries to speed things up while learning core concepts. Testing on a testnet before going live is crucial—trust me, it’s better to catch bugs there than lose real ETH on your first try.
Deploying contracts with Truffle or Hardhat
Truffle and Hardhat are like your smart contract toolkits. They compile, test, and deploy your code, automate repetitive tasks, and hook into wallets like MetaMask. You can simulate a network locally to debug before going live. These frameworks reduce mistakes, optimize gas usage, and streamline interaction. For beginners, pre-built scripts and tutorials make deployment much less intimidating, while still teaching what’s going on under the hood.
Using MetaMask for deployment
MetaMask is your bridge to Ethereum. It safely manages private keys, signs transactions, and handles gas payments. During deployment, it prompts for confirmation at every step, which is a lifesaver for avoiding mistakes. MetaMask also connects you to testnets and Layer 2 solutions, so you can experiment without fear. For beginners, it’s the easiest and safest way to get contracts on-chain without running a full node.
How do smart contracts execute automatically in crypto?
Here’s the cool part: smart contracts run themselves when conditions in the code are met. No middlemen, no human error—just precise execution. In crypto, this powers DeFi loans, token swaps, NFT transfers, and other decentralized operations. The deterministic code makes outcomes predictable and trustless. Developers and users can rely on contracts to enforce agreements without lifting a finger, creating a truly autonomous ecosystem.

Self-executing features of smart contracts
Contracts kick in when triggered by events—receiving tokens, a specific date, or data from an oracle. Once triggered, they handle tasks automatically: calculate interest, execute trades, or distribute staking rewards. This predictability boosts confidence and makes operations smooth across blockchain apps. Honestly, seeing it in action feels like watching magic happen on the blockchain.
The role of oracles in smart contracts
Oracles feed real-world data into smart contracts, letting them interact with events outside the blockchain. For example, an insurance contract can use weather data from an oracle to trigger a payout automatically. Oracles verify information before execution, keeping contracts accurate and secure. Without them, contracts would be stuck in the blockchain world, unable to respond to reality.
Smart contracts in DeFi lending and borrowing
Platforms like Aave and Compound run entirely on smart contracts. They manage deposits, collateral, interest, and repayments automatically. Borrowers and lenders don’t need banks or brokers—the contracts enforce the rules precisely. Automation cuts errors, lowers risk, and makes returns predictable. Essentially, smart contracts create a decentralized financial system that’s transparent, accessible, and efficient.
Practical examples of smart contract execution in crypto
Smart contracts are not just theory—they power real applications in DeFi, NFTs, and token ecosystems. On DEXs, contracts match trades, calculate fees, and transfer assets automatically. NFT platforms mint new tokens and handle royalties. Lending platforms calculate interest, manage collateral, and trigger liquidations without human help. These examples show how contracts operate autonomously, ensuring transparency, security, and reliability. For beginners, understanding these use cases makes the benefits of smart contracts much clearer.
Smart contract use cases table
| Use Case | Description | Example Platforms |
|---|---|---|
| DeFi Lending | Automates borrowing, lending, and collateral management—basically, the contracts act like a 24/7 bank with zero human intervention. | Aave, Compound |
| Token Creation | Defines token rules, supply, and transfer logic—think of it as setting the DNA for your digital asset. | ERC-20, BEP-20 Tokens |
| NFT Transactions | Mints, buys, and sells NFTs, while making sure creators get their royalties automatically—no middlemen needed. | OpenSea, Rarible |
| Supply Chain | Tracks goods, confirms delivery, and triggers payments automatically—keeping everyone honest and reducing errors. | IBM Food Trust, Everledger |
| Decentralized Exchange | Automates token swaps and liquidity provision—your trades happen instantly, fairly, and securely. | Uniswap, SushiSwap |
Security and efficiency considerations
Smart contracts need to be both secure and efficient—no exceptions. They should be audited to avoid nasty bugs like reentrancy attacks, overflow errors, or logical flaws. Writing lean, optimized code also keeps gas costs down, which users definitely appreciate. Testing on Ethereum, BSC, or Solana testnets lets developers catch problems before going live. Following proper security practices isn’t just for pros—even beginners should make it a priority to avoid costly mistakes and protect user trust.
Automation and advanced features in smart contracts
Some smart contracts are downright sophisticated. They use oracles, multi-signature approvals, and automated triggers to do more than simple token transfers. Oracles feed in real-world data—market prices, sports results, weather conditions—so contracts can react automatically. Multi-signature setups require several approvals before execution, adding another security layer. These tools open the door to complex decentralized apps, letting processes run smoothly with minimal human intervention. Honestly, the automation alone is what makes blockchain applications feel futuristic.
Smart contract automation table
| Feature | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Oracles | Feed real-world data into contracts so they can react automatically—like market prices or weather updates. | Chainlink |
| Multi-signature | Requires multiple approvals before a contract can run, adding an extra security layer. | Gnosis Safe |
| Automated Liquidation | Triggers asset liquidation automatically when collateral drops below a set level. | Aave, Compound |
| Yield Farming | Distributes rewards automatically based on staking rules, no manual intervention needed. | Yearn Finance |
| Event Triggers | Executes contract functions when certain conditions are met—customizable for DeFi or NFT apps. | Custom DeFi & NFT contracts |
Conclusion
Smart contracts really showcase the magic of blockchain: automating, securing, and decentralizing processes. From DeFi and NFT marketplaces to supply chains and tokenized ecosystems, they cut out intermediaries, reduce mistakes, and enforce rules consistently. Beginners exploring Ethereum, BSC, Solana, or Cardano can start small—deploy test contracts, experiment, and gradually interact with real applications. Getting a handle on gas, automation, security, and contract execution is key to navigating the crypto world effectively. Master these basics, and you’ll be able to tap into blockchain’s full potential, building and using decentralized systems with confidence—and maybe even a little awe at how smoothly it all runs.
